Why Lemon Juice Is A Risky Alternative For Recharging Batteries
When your batteries run low, the ideal solution is to recharge them using a proper charger or replace them with new ones. Yet, some people explore unconventional ideas, such as using lemon juice to recharge alkaline batteries. While this concept might seem intriguing at first, it's both impractical and potentially dangerous. Here's why.
The idea of using lemon juice stems from the basic science experiment known as the "lemon battery," where lemons, paired with zinc and copper, produce a small electrical charge. While interesting, the power generated by a single lemon is minimal — barely enough to light a small LED. Using lemon juice as a power source poses serious risks, particularly due to its acidic nature.
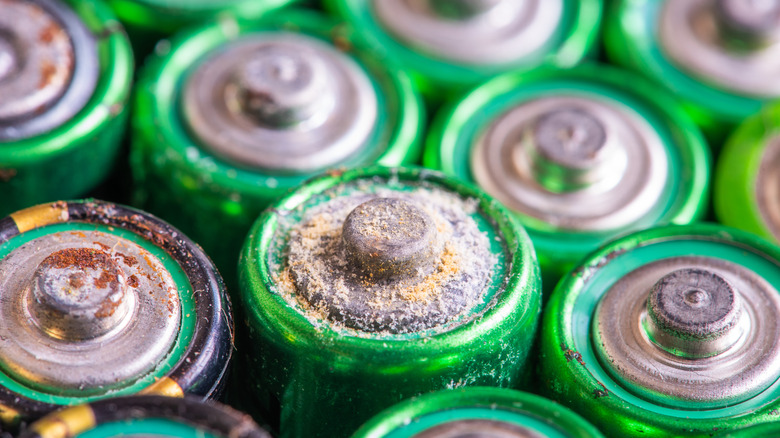
Citric acid in lemon juice can accelerate corrosion in metals, especially when applied to battery terminals or internal components. This corrosion can damage your devices, weaken battery connections, and lead to leakage. Battery leaks are particularly hazardous, as they can release harmful chemicals, such as potassium hydroxide, which can irritate skin and eyes and cause severe burns if mishandled.
Acidic corrosion and safety concerns
Corroded batteries cannot be salvaged for reuse. While you may clean battery corrosion from devices to prevent further damage, the batteries should be thrown away immediately as they may pose ongoing risks. Some DIY enthusiasts suggest mixing lemon juice with other household substances, such as baking soda, in an attempt to enhance its power. However, this is a misunderstanding of basic chemistry. Baking soda, an alkaline compound, neutralizes acids rather than amplifying their effects. When mixed with lemon juice, it forms a neutral solution that is ineffective for charging batteries.
Although lemon juice is often touted as a way to clean battery corrosion, it is not a viable solution for recharging batteries. Recharging a battery requires a specific electrical input to reverse the chemical reactions that occur during discharge. Lemon juice cannot provide the necessary electrical energy or control to achieve this. The risks of corrosion, chemical exposure, and potential device damage far outweigh any perceived benefits. So next time your batteries are running low on juice, it's best to either recharge them regularly or dispose of them properly and find other household uses for lemon juice.